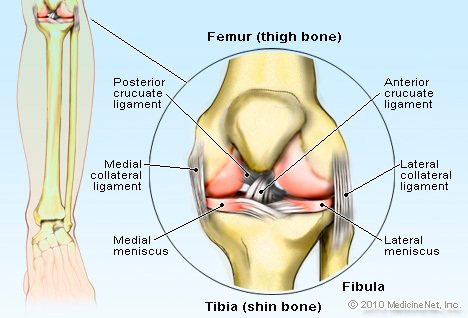
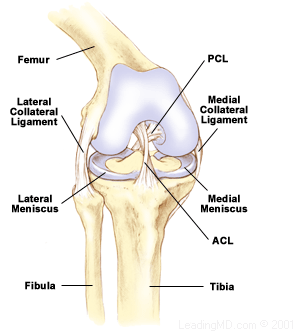
One of the most common injuries of the knee is an Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tear or sprain, with approximately 200,000
ACL injuries a year in the United States. These injuries typically occur when the individual is participating in sports such as skiing, football, basketball and soccer, specifically when changing directions or abrupt stopping or jumping. The ACL acts as a stabilizer in the knee and connects the femur to the tibia. The function of the ligament is to keep the knee from over rotation and extending beyond the normal range of motion.
An immediate, and most common indication of an ACL injury is a popping sound and feeling within the knee cap, with swelling occurring quickly after. To definitively diagnose an ACL injury, you will need to receive an x-ray of the knee. Not all ACL injuries require surgery, some patients are able to recover with rehabilitation and modification of activities, although surgery is often recommended for patients that live an active lifestyle. Injuries are classified in three categories:
The menisci are pieces of cartilage that act as shock absorbers
for your knee and help keep it stable. The two menisci are the medial meniscus and lateral meniscus, the medial is found on the inside while the lateral is on the outside compartment of the knee. There are two types of
meniscus injuries, acute tears and degenerative tears. Acute tears happen when the knee is bent and twisted with force while in a weight bearing position. Degenerative tears are more typical with people over the age of 65 as the meniscus weakens and becomes less elastic over time.
Often when the injury is a result of a trauma while playing sports, in addition to the meniscus being torn there will tend to be other knee injuries as well, such as and ACL tear. Common symptoms of a meniscus tear include pain, swelling, catching of the knee, locking of the knee, feeling of no support in knee and unable to use full range of motion. Pain to the touch of the meniscus is also a sign of a meniscus tear. Depending on the size and location of the tear, your doctor will recommend either non-surgical or surgical treatment methods.
Chondral Defects
A chondral defect is an injury to the articular cartilage that occurs when the individual twists or pivots while the knee is bent, a direct blow to the knee, or degenerative. The articular cartilage is found at the end of each of the bones that make up the knee. A
chondral injury can be accompanied by another injury such as one to the ACL, although often times the patient does not have a single traumatic event that caused the injury and is typically a result of a series of minor injuries over an extended period of time.
Symptoms of a chondral injury are not as prevalent and obvious as other knee injuries, as swelling is typically the main symptom experienced. Small pieces of the cartilage can break off and then float around within the knee. These fragments are the cause of swelling and can cause pain when the individual is walking or climbing stairs for an extended amount of time. The fragments can interfere with the mechanics of the knee, such as getting caught in the joint as it bends causing the knee to lock.
Cartilage is not able to be repaired on its own, so some other form of treatment is needed for these injuries. Treatment for chondral defects ranges widely depending on the extent of the injury. The least invasive treatment is done when the injury is at the end of the femur, while if the injury is on the tibia or patella the surgical procedures are not as effective. Implantation of stem cells has also been used to treat injuries to the cartilage.
Microfracture is a surgical technique that has been developed to treat chondral defects when the injury extends all the way down to the bone. This arthroscopic procedure was first introduced about 20 years ago as a treatment method that uses the body's own healing abilities and provides an enriched environment for tissue regeneration on the chondral surface.
Patellofemorial Pain Syndrome
Patellofemorial pain syndrome is the term used to describe pain that is specific to the front of the knee and kneecap, commonly referred to as
runners knee. The pain is caused by the patella rubbing against the femur which leads to inflammation. Additionally, the rubbing of the bones can cause damage to the articular cartilage.
Non-surgical procedures are often times the solution to patellofemorial pain syndrome, including rehabilitation to strengthen and retrain the muscles, utilizing a brace to better support the knee, or orthotic inserts in shoes to help reduce overpronation.
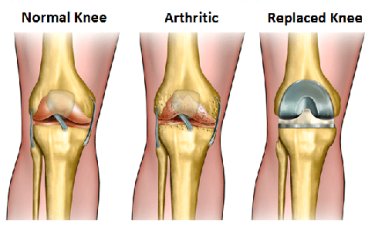
Knee Replacement
A knee replacement is a surgical procedure in which the diseased portions of the bones within the knee are replaced with prosthesis. Knee replacements are typically a solution to pain from one of three types of arthritis - osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and post-traumatic arthritis. Osteoarthritis comes with age and wear of the joint. This type of arthritis will usually affect patients over the age of 50, as the cartilage protecting the bones begins to wear away causing the bones to run against one another. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common of the three types of arthritis and is a result of inflammation. Post-traumatic arthritis is a result of a serious knee injury which fractures the bones and causes damage to the ligaments and cartilage over a period of time. To measure the severity of the arthritis, there are four grades that classify the extent of the injury:
-
Grade I - Early changes show fissuring (breaks) in the cartilage
-
Grade II - More extensive full thickness breaks in the cartilage
-
Grade III - Intermittent loss of cartilage with breaks
-
Grade IV - Exposed subchondral (below the cartilage) bone
Deciding on getting a
total knee replacement is a decision you should not take lightly and should have a thorough discussion with your surgeon. Individuals that benefit from a knee replacement suffer from severe pain or stiffness that hinders their daily activities, such as walking, sitting, standing and going up stairs. Pain is also present when resting, as well as inflammation and swelling that does not decrease. Recovery from a knee replacement includes significant physical therapy that begins one to two days following the surgery, a walking aid such as crutches or a walker, and anti-inflammatory medications.